Plant Propagation
Asexual propagation is any method used to separate part of a plant from its parent, usually to create more genetically identical plants to preserve their desirable characteristics.
The specific method of this propagation is far ranging and depends on the type of plant to propagate. This may be a tree, shrub, or herbaceous perennial, and based on their growth habit or root storage organ. Methods may include division, stem cuttings, leaf cuttings, and layering. Each type requires a set of conditions to be met to ensure new plants are created and thrive. While propagation by division is the easier method, as each plant separated from the parent already has its own roots, other types of propagation usually require the newly removed plant part to be rooted in some fashion.
Some types of propagation include:
ASEXUAL or CLONAL PROPAGATION
Method of producing a new plant from an existing and genetically identical parent plant.
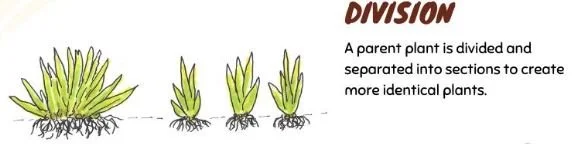
DIVISION:
A parent plant is divided and separated into sections to create more identical plants.
STEM CUTTING:
A stem portion of a plant is cut off from a parent and rooted to make a new identical plant.
NODAL VS INTERNODAL STEM CUTTING:
A Nodal cutting is a cutting with a cut just below a node on a stem.
An Internodal cutting is a cut made on the stem between nodes.
LEAF CUTTING:
A leaf cutting is a removed leaf that is rooted to make a new identical plant.
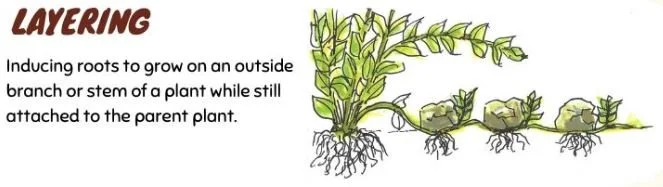
LAYERING:
Inducing roots to grow on an outside branch or stem of a plant while still attached to the parent plant.
For more information, try these resources:
https://content.ces.ncsu.edu/extension-gardener-handbook/13-propagation
https://durhammastergardeners.com/2025/02/12/propagating-trees-shrubs-through-hardwood-cuttings/
https://ucanr.edu/sites/EDC_Master_Gardeners/files/175642.pdf
https://www.pubs.ext.vt.edu/426/426-002/426-002.html
https://extension.missouri.edu/publications/mg3